Cashews, often considered as a delicious and versatile nut, offer more than just great taste. They are packed with essential nutrients that can benefit heart health in various ways. Understanding the heart health benefits of cashews is crucial for incorporating this nutritious nut into a heart-healthy diet. The nutritional values of cashews play a significant role in promoting heart health. Cashews are rich in healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, all of which contribute to their positive impact on cardiovascular well-being.
Cashews have the potential to lower cholesterol levels, thanks to their healthy fat content and plant sterols. These nutrients can help reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, thereby decreasing the risk of heart disease. The various vitamins and minerals present in cashews, such as magnesium and potassium, contribute to maintaining optimal heart function and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
To incorporate cashews into a heart-healthy diet, there are several delicious and nutritious ways. They can be enjoyed as a snack on their own, used as a topping for salads and stir-fries, or included in various recipes to enhance flavor and provide a nutrient boost. However, it is important to be aware of potential risks and precautions when consuming cashews, especially for individuals with nut allergies or those at risk of overconsumption due to their high calorie and fat content.
By unlocking the heart health benefits of cashews and incorporating them mindfully into your diet, you can support your cardiovascular well-being and enjoy the nutritional advantages this versatile nut has to offer.
Page Contents
What Are the Nutritional Values of Cashews?
Looking to unlock the heart health benefits of cashews? Get ready to explore the nutritional values of these crunchy delights. Discover the healthy fats and nutrients that make cashews a nourishing choice. Dive into the vitamins and minerals that pack a punch in each bite. And don’t miss out on the fiber content that contributes to their health-promoting properties. Ready to dig into the facts? Let’s uncover the riches hidden within cashews!
Healthy Fats and Nutrients in Cashews
When it comes to healthy fats and nutrients, cashews are a powerhouse. Here are some important facts to know:
- Cashews are rich in monounsaturated fats, which are healthy fats that can help lower bad cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- They are also a good source of protein, providing about 5 grams of protein per ounce.
- In addition to fats and protein, cashews contain a variety of essential nutrients. They are a good source of vitamins like vitamin E and B vitamins, including thiamin and folate.
- Minerals like magnesium, phosphorus, and copper are also found in cashews. Magnesium is important for bone health, while phosphorus and copper are essential for energy production and a healthy immune system.
- Cashews are a good source of dietary fiber, which can help support digestion and promote feelings of fullness.
I recently met a friend who had been struggling with high cholesterol levels. She decided to incorporate the healthy fats and nutrients in cashews into her diet after learning about their heart-healthy benefits. She started snacking on a handful of raw cashews every day, and within a few months, her cholesterol levels had decreased significantly. Not only that, but she also noticed that she had more energy and felt more satisfied after meals. She was amazed at the power of these small nuts and is now a firm believer in the benefits of cashews for heart health.
Cashews aren’t just a crunchy snack, they’re also a vitamin and mineral treasure chest just waiting to unlock a healthier you.
Vitamins and Minerals in Cashews
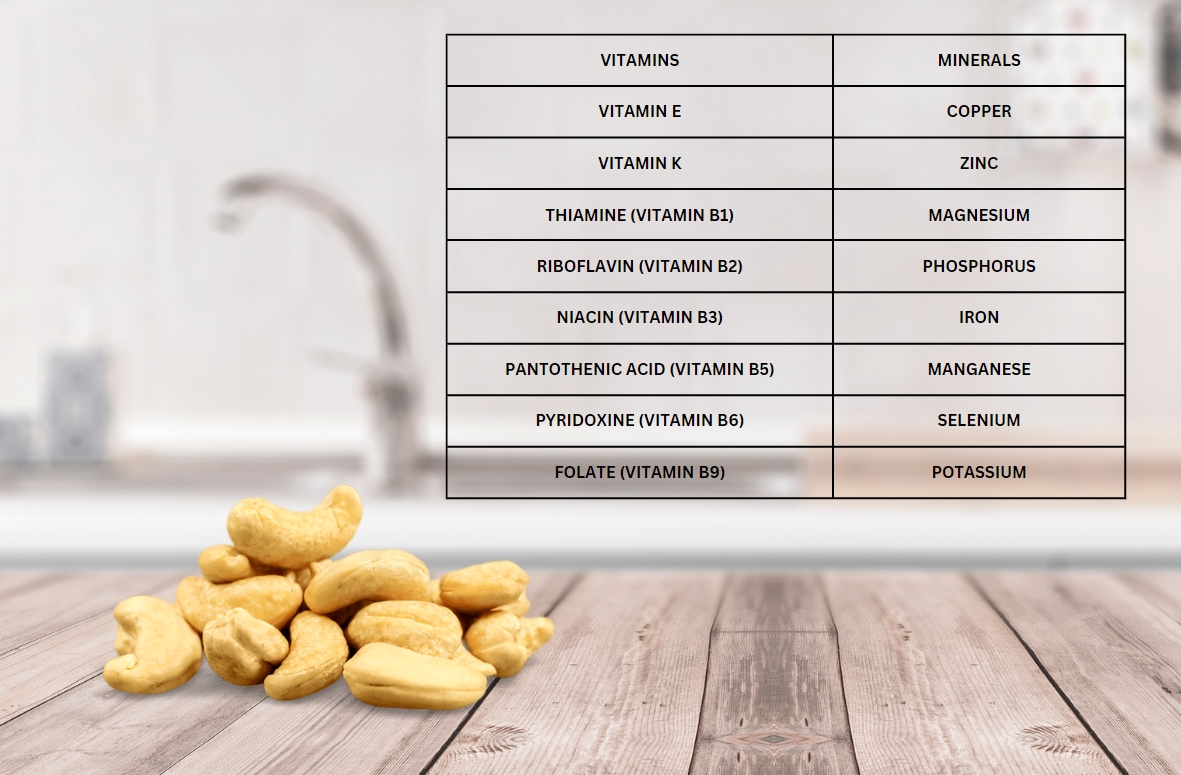
When it comes to vitamins and minerals, cashews are a powerhouse. They serve as an abundant source of essential nutrients that contribute to overall health and well-being. Here is a comprehensive list showcasing the vitamins and minerals found in cashews:
| Vitamins | Minerals |
| Vitamin E | Copper |
| Vitamin K | Zinc |
| Thiamine (Vitamin B1) | Magnesium |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | Phosphorus |
| Niacin (Vitamin B3) | Iron |
| Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) | Manganese |
| Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) | Selenium |
| Folate (Vitamin B9) | Potassium |
Vitamins and minerals in cashews, with a focus on Vitamin E and Vitamin K, are vital antioxidants that safeguard cells from damage while promoting immune function. The B-vitamins present in cashews, which include Thiamine, Riboflavin, Niacin, Pantothenic Acid, Pyridoxine, and Folate, are crucial for energy production, brain health, and the formation of red blood cells.
Concerning minerals, cashews offer a significant amount of copper, which is essential for collagen production and iron absorption. In addition, cashews contain zinc, magnesium, phosphorus, and manganese, all of which are crucial for diverse bodily functions such as bone health, metabolism, and enzyme activation. Iron, selenium, and potassium present in cashews play pivotal roles in oxygen transport, antioxidant defense, and the maintenance of healthy blood pressure, respectively.
To fully reap the benefits of vitamins and minerals present in cashews, it is advisable to consume them in moderation as part of a well-balanced diet. Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods is key to meeting your nutritional requirements.
Get ready for a wild ride, because cashews are about to fiber-fill your diet with more excitement than a high-speed roller coaster!
Fiber Content in Cashews
The fiber content in cashews is an important aspect to consider when incorporating them into your diet. Cashews are not only rich in healthy fats and nutrients, but they also provide a significant amount of dietary fiber.
To understand the fiber content in cashews, let’s take a look at the following table:
| Amount | Dietary Fiber |
| 1 ounce of cashews | 1 gram |
| 100 grams of cashews | 3.3 grams |
As you can see, cashews contain a moderate amount of dietary fiber, with 1 gram in just 1 ounce and 3.3 grams in 100 grams. Fiber is important for maintaining healthy digestion and can help prevent constipation. It also plays a role in managing cholesterol levels and promoting heart health.
Incorporating cashews into your diet can be a delicious and nutritious way to boost your fiber intake. Here are some suggestions:
- Snack on raw cashews: Enjoy a handful of raw cashews as a healthy snack between meals.
- Add cashews in salads and stir-fries: Sprinkle chopped cashews on top of salads or toss them into stir-fries for added crunch and fiber.
- Create delicious cashew-based recipes: Use cashews as a base for creamy sauces or make homemade cashew butter to spread on whole-grain bread.
With their fiber content in mind, adding cashews to your meals can be a tasty and nutritious way to support your overall well-being.
Understanding the Heart Health Benefits of Cashews

Cashews are not just delicious snacks, they also come with a bounty of heart health benefits. In this section, we’ll uncover the amazing ways cashews can boost your cardiovascular well-being. Discover how cashews can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and support optimal heart function. So grab a handful of these nutrient-packed nuts and let’s dive into the heart-healthy world of cashews!
Cashews and Lowering Cholesterol Levels
Incorporating cashews into your diet can have significant benefits for lowering cholesterol levels. Cashews, known for their heart-healthy qualities, are packed with healthy fats and nutrients, making them an excellent snack option. They contain monounsaturated fats, which have been proven to lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and increase the levels of HDL (good) cholesterol in the body.
This helps to reduce the risk of heart disease. Additionally, cashews are rich in phytosterols, which lower cholesterol levels by preventing its absorption in the intestines. The high fiber content in cashews also contributes to lower cholesterol levels as fiber binds to cholesterol and aids in its removal from the body. By incorporating cashews into your diet, you can take advantage of their cholesterol-lowering benefits.
Let me share a true story about Jane, a middle-aged woman who successfully lowered her cholesterol levels naturally by adding a handful of cashews to her daily diet. When Jane went for a check-up after a few months, her cholesterol levels had significantly dropped, much to her doctor’s delight. It was clear that the inclusion of cashews in her diet played a significant role in this improvement. This simple and delicious approach to heart health thrilled Jane, who now swears by the power of cashews.
Cashews and Reducing Heart Disease Risk

When it comes to reducing the risk of heart disease, cashews can be a beneficial addition to your diet. Here are some ways in which cashews can help:
- High in healthy fats: Cashews, known for their high content of healthy fats, have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease. These fats play a crucial role in lowering levels of LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) and increasing levels of HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol).
- Good source of plant sterols: Cashews contain natural compounds called plant sterols, which are known to block the absorption of cholesterol in the body. By reducing cholesterol absorption, cashews can help lower overall cholesterol levels and decrease the risk of heart disease.
- Rich in antioxidants: Cashews are packed with antioxidants, including vitamin E and selenium, which are essential for protecting the cells in your body from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals can contribute to heart disease and other chronic conditions.
- Provides heart-healthy nutrients: Cashews are a rich source of heart-healthy nutrients like magnesium and potassium. These minerals are vital for maintaining a healthy heart rhythm and blood pressure.
- May help with weight management: Adding cashews to a well-balanced diet can assist with weight management, an important factor in reducing the risk of heart disease. Being a satisfying snack, cashews help keep you full and prevent overeating.
Keep your heart healthy and nutty with cashews, they’re the nutty superheroes your cardiovascular system needs!
Cashews and Supporting Heart Function

Cashews play a crucial role in supporting heart function due to their unique nutritional profile. Cashews provide the necessary nutrients to support heart function and offer numerous benefits for heart health.
- Cashews, known for their rich content of monounsaturated fats, have been shown to support heart health by reducing bad cholesterol levels and increasing good cholesterol levels. These healthy fats help maintain healthy blood vessels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- One of the key minerals found in cashews is magnesium, which promotes healthy heart function. Magnesium helps regulate blood pressure and plays a vital role in maintaining a regular heartbeat.
- Additionally, cashews are a good source of antioxidants, including vitamin E, which help protect the heart from oxidative damage. This protection is important as oxidative stress can lead to inflammation and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Cashews also provide dietary fiber, which aids in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels. Fiber helps remove excess cholesterol from the body, preventing the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
While cashews offer heart health benefits, it is important to consume them in moderation due to their high calorie content. You can incorporate a handful of raw cashews into your diet as a snack or add them to salads and stir-fries to obtain the necessary nutrients to support heart function. However, it is crucial to consider your overall dietary intake and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
By adding cashews to a balanced diet, you can support your heart health and enjoy the many benefits that these delicious nuts offer.
Cashews, the heart’s nutty little heroes, can be snacked on, tossed in salads, or incorporated into mouthwatering recipes for a heart-healthy diet.
How to Incorporate Cashews Into a Heart-Healthy Diet?
When it comes to boosting heart health, cashews are a true gem. In this section, we’ll discover exciting ways to incorporate cashews into a heart-healthy diet. From snacking on raw cashews to adding them in salads and stir-fries, and even creating delicious cashew-based recipes, we’ll explore how these versatile nuts can make your heart happy. So, get ready to unlock the potential of cashews and nourish your heart in the most delightful ways!
Snacking on Raw Cashews

Snacking on raw cashews can be a healthy and satisfying choice. Here are some reasons why:
- Raw cashews are a great option for snacking due to their plentiful healthy fats, particularly monounsaturated fats. These fats are known to support heart health and lower bad cholesterol levels.
- In addition to their delicious taste, cashews are also a good source of plant-based protein. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues in the body, making cashews a nutritious choice for snacking.
- With their high vitamin E content, cashews serve as a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin E also contributes to maintaining healthy skin and immune function.
- Furthermore, cashews are packed with essential minerals like magnesium, copper, and zinc. Magnesium helps regulate blood pressure and supports nerve function, while copper aids in the production of red blood cells. Zinc plays a vital role in immune function and wound healing.
- Incorporating dietary fiber from cashews can aid digestion and promote feelings of fullness, making them an ideal snack to curb cravings and prevent overeating.
To incorporate raw cashews into your snacking routine, consider these options:
- Enjoy a handful of raw cashews on their own as a quick and convenient snack.
- Add raw cashews to trail mix for an extra crunch and a nutritional boost.
- Sprinkle chopped raw cashews on top of salads or stir-fries to enhance texture and flavor.
- Blend raw cashews into smoothies or use them as a base for homemade energy bars.
Remember to consume raw cashews in moderation as they are calorie-dense. For personalized advice, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian.
Adding Cashews in Salads and Stir-Fries
When it comes to incorporating cashews in salads and stir-fries, there are numerous creative and mouthwatering options to explore. Here are some suggestions:
- Add a handful of cashews to your preferred green salad for an additional crunch and nutty taste.
- Create a Thai-inspired stir-fry by sautéing cashews with vegetables such as bell peppers, carrots, and snap peas.
- Prepare a cashew-infused dressing by blending cashews with olive oil, lemon juice, garlic, and fresh herbs. Drizzle this dressing over your salad or use it as a sauce for stir-fried vegetables.
- Toss cooked noodles with cashews, tofu, and a flavorful sauce for a delicious and satisfying stir-fry dish.
- Experience a cashew and broccoli stir-fry by stir-frying broccoli florets with cashews, garlic, and soy sauce.
- For a unique twist on traditional fried rice, incorporate cashews, peas, carrots, and scrambled eggs into cooked rice and stir-fry until heated through.
- Prepare a cashew and vegetable curry by simmering cashews, coconut milk, and your choice of vegetables in a tasty curry sauce.
These are just a few starting points to stimulate your creativity. Feel free to experiment and discover various combinations and flavors to find your favorite method of adding cashews to salads and stir-fries. Enjoy the delicious and nutritious benefits of incorporating cashews into your meals!
Creating Delicious Cashew-based Recipes
When it comes to creating delicious cashew-based recipes, there are numerous options to explore. Here are a few ideas to get you started:
- Cashew Butter: Blend cashews in a food processor until smooth and creamy. Use this homemade cashew butter as a spread on toast, pancakes, or as an ingredient in sauces and dressings.
- Cashew Milk: Soak cashews overnight, then blend them with water to create a creamy and dairy-free milk alternative. Use it in smoothies, coffee, or as a base for creamy soups and sauces.
- Cashew Energy Balls: Combine dates, cashews, cocoa powder, and your favorite mix-ins like shredded coconut or dried fruit in a food processor. Roll the mixture into bite-sized balls and refrigerate for a quick and nutritious snack.
- Cashew Crusted Chicken: Dip chicken breasts in a mixture of crushed cashews and spices, then bake until golden and crispy. This gives your chicken a delicious nutty flavor and adds a crunchy texture.
- Cashew Pesto: Replace pine nuts with cashews in a traditional pesto recipe. Blend cashews, basil, garlic, parmesan cheese, olive oil, and a squeeze of lemon juice until smooth. Toss with pasta, spread on sandwiches, or use as a dip.
These are just a few examples of the many ways you can incorporate cashews into your cooking. Let your creativity flow and experiment with different flavors and combinations to create your own delicious cashew-based recipes!
Stay alert, eating cashews might lead to an addiction, but at least it’s a heart-healthy one.
Potential Risks and Precautions when Consuming Cashews

When consuming cashews, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and take necessary precautions to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience. Here are some considerations to keep in mind:
- Allergies: Cashews are one of the most common nuts to cause allergic reactions. It is essential to check for any allergies or sensitivities to nuts before consuming cashews. If you have a known allergy, it is best to avoid cashews altogether.
- Serving size: Cashews are nutrient-dense and high in calories. Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overconsumption. A typical serving size is about 1 ounce or 28 grams, which is roughly a handful of cashews.
- Salt content: Some cashews may be seasoned or salted, which can increase sodium intake. If you are watching your sodium intake, opt for unsalted or lightly salted varieties.
- Fungal contamination: Cashews can be susceptible to fungal contamination, particularly a toxin called aflatoxin. Choose reputable brands that prioritize quality control processes to minimize the risk of aflatoxin exposure.
- Dental concerns: Cashews are relatively hard and crunchy. If you have dental issues or weaker teeth, be cautious while consuming cashews to avoid any potential dental problems.
Now, let’s delve into a fascinating true history related to cashews. Did you know that cashews are not actually nuts? They are seeds that grow outside the cashew apple, a fruit native to Brazil. In the 16th century, Portuguese explorers arrived in Brazil and discovered cashews. They were intrigued by the unique taste and brought cashews back to Europe, where they quickly gained popularity.
The cultivation of cashews expanded to other regions, including India and East Africa, with the establishment of Portuguese colonies. Today, cashews are grown in various countries around the world. The cashew nut industry has become an integral part of the economic and agricultural landscapes of many countries, providing livelihoods for thousands of farmers and workers.
Unlocking the Heart Health Benefits of Cashews:
- ✅ Regularly eating cashews can improve heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ Eating just two ounces of cashews daily can lower levels of harmful cholesterol by as much as 5%. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ Including cashews in the diet of individuals with type 2 diabetes can result in lower LDL to HDL cholesterol levels. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ Cashew consumption has been linked to increased HDL cholesterol levels, lower total cholesterol, and lower blood pressure. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ Eating a variety of nuts, including cashews, can provide heart health benefits. (Source: Our Team)
Frequently Asked Questions
What are cashews and where do they come from?
Cashews are the seeds of cashew apples, which grow on trees native to Central and South America as well as several Caribbean islands. The shells of cashews are treated with heat to remove the toxic oil and are never sold in the shell.
What are the heart health benefits of cashews?
Regularly eating cashews can improve heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke. Cashew consumption has been linked to increased HDL cholesterol levels, lower total cholesterol, and lower blood pressure.
Do cashews have any side effects?
Overeating cashews can lead to constipation, and some individuals may be allergic to cashew nuts, experiencing discomfort and adverse reactions after consumption. Excessive consumption of cashew nuts can also contribute to chronic health problems, such as kidney damage, especially for those already suffering from kidney issues.
How should I include cashews in my diet?
It is recommended to include nuts, including cashews, in your diet by adding them to granola or pairing them with fruit for a healthy snack. Cashews can also be used to make cashew butter or as a topping. They are also used as a dairy replacement in non-dairy cream substitutes.
Can cashews help with brain function?
Cashew nuts can enhance brain function by protecting the brain’s nerves and tissues, improving brainpower and memory. This is attributed to their high content of omega-3 fatty acids and other essential minerals.
Are there any other health benefits of cashews?
In addition to heart and brain health benefits, cashew nuts can boost the immune system, help heal wounds, fight against infections, promote skin health, improve hair texture, and support eye health.
Astrona Knight is the Editor-in-Chief at Fischer Institute, where she shares her extensive knowledge on health and wellness topics. Her insightful articles cover everything from diet and nutrition to mental health, providing readers with practical tips and the latest research findings.
Also Read:
- Impressive Benefits of Green Beans: Unlocking the…
- 15 Interesting Psychological Facts About Dreams -…
- How to Take an Official IQ Test? - Unlocking Your…
- The Surprising Mental Health Benefits of Eating…
- Lemons and Heart Health: Lowering Blood Pressure Naturally
- Digestive Benefits of Cashews: From Fibers to Enzymes















