Pistachio, a tasty and nutritious nut from the pistachio tree, belongs to the cashew family. Originally from Asia, pistachios are now cultivated and enjoyed in numerous regions worldwide. Rich in vital nutrients, pistachios offer a multitude of health and beauty advantages. Nevertheless, consuming excessive amounts of pistachios can lead to certain side effects, which will be discussed in this article.
Page Contents
- 1 Nutritional Value of Pistachios
- 2 Side Effects of Overconsuming Pistachios
- 2.1 Promote Weight Gain
- 2.2 High Blood Pressure
- 2.3 Gastrointestinal Problems
- 2.4 Nut Allergic Reactions
- 2.5 Bad For People Suffering From Kidney Problems
- 2.6 May Increase The Risk Of Kidney Stones
- 2.7 Aflatoxin Allergy
- 2.8 Risk Of Being Contaminated By Navel Orangeworm (NOW)
- 2.9 Risk Of Being Contaminated By Bacterium Salmonella
- 2.10 Increased Risk Of Pesticides And Insecticides
- 2.11 Increased Risk Of Acrylamide
- 2.12 High Manganese Risk
- 2.13 Too Much Fiber Is Bad For Stomach
- 3 FAQs
- 3.1 How many pistachios should you eat in a day?
- 3.2 Is it OK to eat them every day?
- 3.3 Why are pistachios so bad for you?
- 3.4 Is it good for sperm?
- 3.5 What are the worst nuts to eat?
- 3.6 Are pistachios good for skin?
- 3.7 Are they good for sleep?
- 3.8 How many pistachios should I eat to lose weight?
- 3.9 Does pistachio increase blood sugar?
- 3.10 Are they good for hormones?
- 3.11 Is pistachio good for pregnant ladies?
- 3.12 How many a day is too much?
- 4 Final Words
Nutritional Value of Pistachios
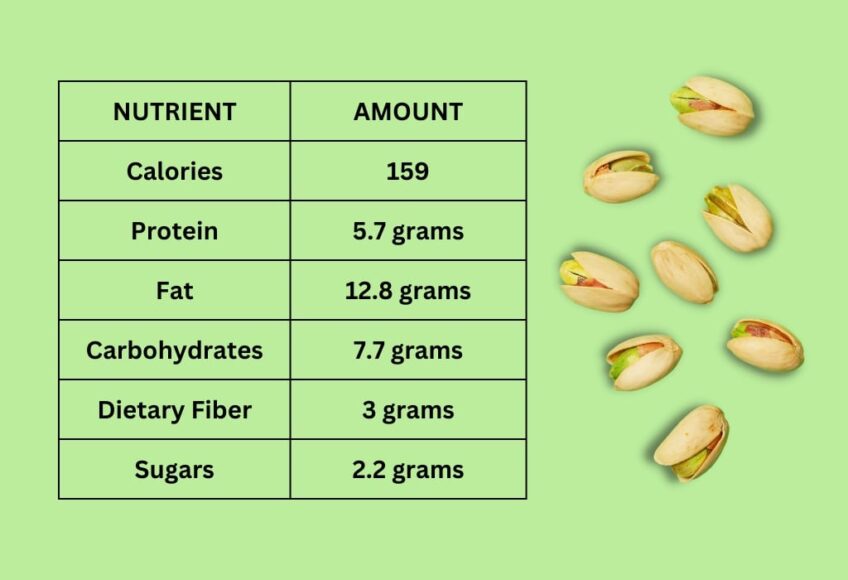
Pistachios are a nutrient-dense nut, providing a variety of essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. Here is a breakdown of the nutritional value of pistachios per 1 ounce (28 grams) serving:
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 159 |
| Protein | 5.7 grams |
| Fat | 12.8 grams |
| Carbohydrates | 7.7 grams |
| Dietary Fiber | 3 grams |
| Sugars | 2.2 grams |
Vitamins and minerals present in pistachios include:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
- Folate
- Thiamin
- Riboflavin
- Niacin
- Pantothenic acid
- Choline
- Betaine
- Calcium
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Zinc
- Copper
- Manganese
- Selenium
Pistachios also contain antioxidants, such as lutein and zeaxanthin, which promote eye health.
Side Effects of Overconsuming Pistachios
Some major pistachios’ side effects are as follows.
Promote Weight Gain
Consuming pistachios in moderation can aid in weight loss, as their dietary fiber content helps maintain satiety and curb overeating, a significant contributor to obesity. They make a fantastic snack and supply us with energy.
However, pistachios are calorie-dense, and overindulging in them may lead to weight gain due to their high caloric content. Consuming 100 grams of pistachios provides 562 calories, meeting over 25 percent of the daily calorie needs of the body. Additionally, pistachios are sometimes salted to improve taste and encourage overconsumption (for sales purposes).
To effectively manage your weight, enjoy pistachios in moderation and avoid salted varieties.
High Blood Pressure
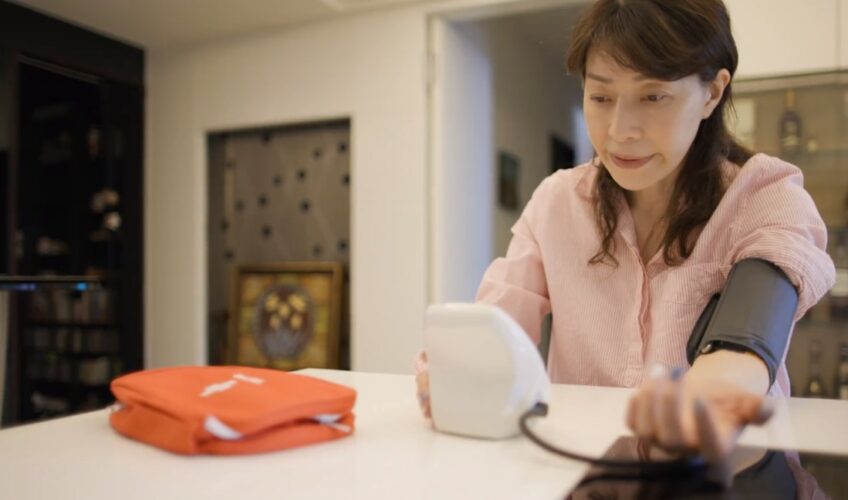

Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a prevalent health issue affecting millions worldwide and is a primary contributor to cardiovascular complications.
Pistachios are rich in potassium, a natural vasodilator that relaxes blood vessels, enhances blood circulation, and alleviates hypertension or high blood pressure.
However, excessive consumption of pistachios may cause blood pressure to drop below the healthy range, leading to symptoms such as lightheadedness, nausea, blurred vision, confusion, general weakness, and fainting. Conversely, salted and roasted pistachios typically have high sodium and fat content, potentially increasing the risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular issues.
To maintain your health, consume unsalted pistachios in moderation and avoid salted varieties.
If you are taking blood pressure medication, consult your doctor before incorporating any type of pistachios into your diet to prevent potential food-drug interactions.
Gastrointestinal Problems
The dietary fibers in pistachios serve as a natural laxative, promoting bowel movement and alleviating constipation and other digestive issues such as abdominal pain, gas, bloating, and flatulence.
Nevertheless, overconsuming pistachios can overstimulate the bowel, resulting in intestinal gas, blockage, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
Additionally, “fructan” found in pistachios may trigger allergic reactions in some individuals, leading to gastrointestinal problems such as bloating, diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, and abdominal pain.
Nut Allergic Reactions
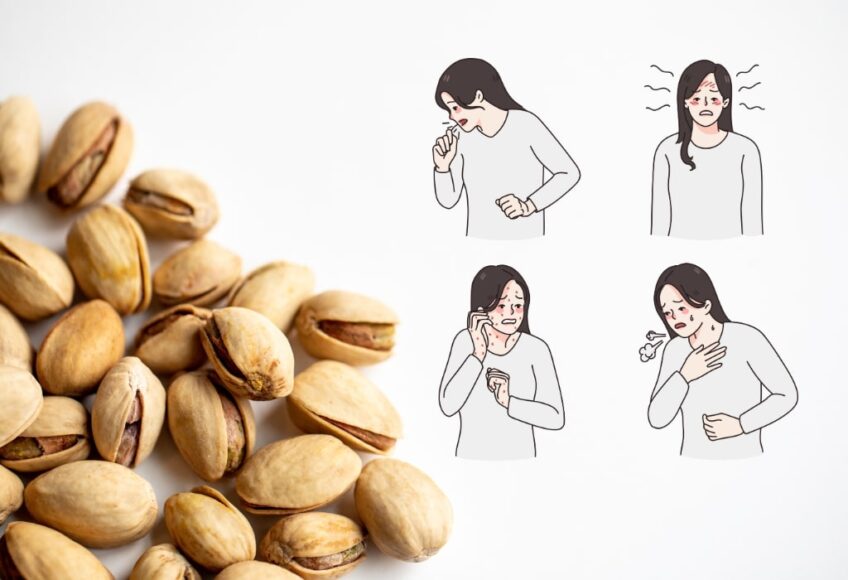

Steer clear of pistachios if you have a tree nut allergy.
People who are allergic to tree nuts such as almonds, walnuts, cashews, and hazelnuts may also be allergic to pistachios. Tree nut allergies can lead to symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, cramps, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, itching in the mouth, throat, eyes, skin, and other areas, nasal congestion, and trouble breathing.
In severe cases, tree nut allergies can result in anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening allergic reaction.
Bad For People Suffering From Kidney Problems
Pistachios are a source of potassium, an essential mineral that helps regulate blood pressure and offers additional benefits such as relieving stress and anxiety, enhancing metabolism, maintaining electrolyte balance, improving nerve functions, and reducing the risk of heart and kidney disorders.
Nonetheless, consuming excessive amounts of pistachios can lead to an overload of potassium in the kidneys, making it challenging for them to eliminate the surplus potassium.
Elevated potassium levels may raise the risk of nausea, weakness, slow pulse, irregular heartbeat, heart failure, dehydration, type-1 diabetes, Addison’s disease, and internal bleeding.
May Increase The Risk Of Kidney Stones
Pistachios contain moderate levels of oxalates and methionine.
Overconsuming pistachios may heighten the risk of kidney stones, as the oxalates in pistachios can bind with minerals like calcium and potassium, forming calcium oxalate and potassium oxalate crystals.
Additionally, methionine in pistachios can be converted to cysteine, which may lead to the formation of cystine kidney stones.
Aflatoxin Allergy
Pistachios are susceptible to contamination by aflatoxin, a carcinogenic substance produced by the fungus Aspergillus flavus when pistachios are grown or stored in moist and warm environments.
Long-term consumption of pistachios contaminated with aflatoxin may elevate the risk of liver cancer and hepatitis B.
Roasting pistachios can considerably lower the risk of aflatoxin contamination.
Risk Of Being Contaminated By Navel Orangeworm (NOW)
Pistachios are vulnerable to contamination by the Navel Orangeworm (NOW), which can be found in the pistachio seed or between the seed and the shell.
This cream-colored, orange, or red worm, measuring approximately 25 mm in length, can damage the nutmeat of pistachios.
Pistachios contaminated by the Navel Orangeworm have an increased risk of being contaminated by Aspergillus fungi, which produce aflatoxin.
Risk Of Being Contaminated By Bacterium Salmonella
Pistachios are also more susceptible to contamination by the bacterium Salmonella.
Salmonella can cause diarrhea, fever, and gastrointestinal issues, and may be fatal for infants, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Appropriate roasting of pistachios can eliminate Salmonella bacteria; however, improper roasting could lead to contamination of previously uncontaminated pistachios (due to contact with contaminated ones).
Increased Risk Of Pesticides And Insecticides
Pistachios are often treated with pesticides and insecticides to protect them from the attacks of pests and insects.
Consuming pesticides laden pistachios without thoroughly cleaning them may cause vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, and other allergic reactions.
Increased Risk Of Acrylamide
Roasting pistachios reduce the risk of aflatoxin and salmonella bacteria, but during the roasting process pistachios form acrylamides.
Acrylamide is a probable carcinogen that may increase the risk of cancers in humans.
High Manganese Risk

Pistachios contain manganese, a trace mineral that aids in the formation of connective tissues, facilitates calcium absorption, regulates blood sugar, metabolizes fats and carbohydrates, and supports proper thyroid gland function, among other benefits.
However, excessive manganese intake can cause headaches, tremors, loss of appetite, leg cramps, hallucinations, and neurological disorders.
Foods rich in manganese may not be suitable for individuals with Parkinsonism, hypermagnesemia, polycythemia, and chronic liver diseases, among other conditions.
Consume pistachios in moderation to avoid the risk of manganese overload.
If your diet already provides sufficient manganese or if you are taking manganese supplements, monitor your pistachio intake carefully.
Too Much Fiber Is Bad For Stomach
The laxative properties of dietary fibers in pistachios enhance bowel movement and alleviate constipation, as well as other digestive issues such as abdominal pain, gas, bloating, and flatulence.
Nonetheless, consuming excessive amounts of dietary fibers can overstimulate the bowel and raise the risk of diarrhea.
It may also lead to intestinal gas, intestinal blockage, abdominal pain, and impaired nutrient absorption, among other issues.
FAQs

How many pistachios should you eat in a day?
To enjoy the delicious taste and health benefits of pistachios, it’s generally recommended to have about 1 ounce (28 grams) or a small handful (around 30-50 nuts) per day. This way, you can relish their delightful flavor without overindulging.
Is it OK to eat them every day?
Absolutely! Including pistachios in your daily diet is a fantastic idea, as long as you consume them in moderation and as part of a well-balanced diet. These little green gems offer a variety of health benefits that can be enjoyed daily.
Why are pistachios so bad for you?
Contrary to popular belief, pistachios aren’t inherently bad for you. However, like with any food, overconsumption or indulging in salted and heavily processed versions can lead to negative health effects. Stick to moderate portions of raw or dry-roasted varieties for the best health benefits.
Is it good for sperm?
Pistachios are packed with antioxidants, which can contribute to improved sperm health and overall reproductive function. So, incorporating these tasty nuts into your diet might just give your fertility a little boost!
What are the worst nuts to eat?
There isn’t a specific type of nut that is considered the “worst” to eat. However, it’s important to enjoy nuts in moderation and choose unsalted, raw, or dry-roasted varieties to reap the maximum health benefits.
Are pistachios good for skin?
Absolutely! Pistachios contain skin-loving antioxidants, healthy fats, and essential vitamins that can help improve your skin’s overall health and appearance. So go ahead and snack on these green beauties for a radiant complexion.
Are they good for sleep?
Interestingly, pistachios contain a small amount of melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate sleep. While their effect on sleep may vary between individuals, enjoying a small serving of pistachios in the evening might just help you drift off to dreamland more easily.
How many pistachios should I eat to lose weight?
When it comes to weight management, aim for around 1 ounce (28 grams) or a small handful (approximately 30-50 nuts) of pistachios per day. Enjoy them as part of a balanced diet, and you might just notice the difference in your waistline!
Does pistachio increase blood sugar?
Good news for those watching their blood sugar levels: pistachios have a low glycemic index, which means they’re less likely to cause significant blood sugar spikes when consumed in moderation.
Are they good for hormones?
Pistachios are rich in nutrients that can support hormone balance, including healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. So, snacking on these delectable nuts might just help keep your hormones in check!
Is pistachio good for pregnant ladies?
Pistachios can be a nutritious and satisfying snack for expectant mothers when consumed in moderation, as they provide essential nutrients needed during pregnancy. However, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice based on your unique needs.
How many a day is too much?
It’s best to stick to around 1 ounce (28 grams) or a small handful (approximately 30-50 nuts) of pistachios per day to avoid overconsumption. By enjoying these tasty nuts in moderation, you’ll be able to savor their delightful flavor and health benefits without going overboard.
Final Words
In conclusion, pistachios are incredibly nutritious and beneficial for our health due to their abundance of essential nutrients such as vitamins C and E, folate, protein, fiber, and minerals.
Furthermore, they are packed with powerful antioxidants like flavonoids, beta-carotene, zeaxanthin, anthocyanins, and proanthocyanidins.
These nutrients work together to combat inflammation, lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases, enhance sleep quality, aid digestion, and support weight loss.
However, it’s crucial to remember that moderation is key. Consuming a small handful (around 30 grams) of pistachios daily can help you reap all their health benefits.
Overindulging in pistachios can lead to several side effects, including allergies, weight gain, increased cancer risk, kidney stones, digestive issues, and high blood pressure.
By enjoying pistachios in moderation, you can experience their numerous health advantages while steering clear of any potential adverse effects.
Theodore is a prolific author at Fischer Institute, known for his insightful articles on health and nutrition. His expertise spans a wide range of topics, from the benefits of traditional foods to the latest in health trends, always aiming to educate and empower readers towards better wellbeing.
Also Read:
- Overload: Major Side Effects of Eating Too Many…
- Major Side Effects of Eating Too Many Mung Bean…
- Major Side Effects OF Eating Too Many Blueberries -…
- Major Side Effects Of Eating Too Many Cashews:…
- 8 Major Side Effects Of Eating Too Much Spinach: The…
- Major Eggplant Side Effects - Take Care of Your Health















